Publication Information
ISSN: 2641-6816
Frequency: Continuous
Format: PDF and HTML
Versions: Online (Open Access)
Year first Published: 2018
Language: English
| Journal Menu |
| Editorial Board |
| Reviewer Board |
| Articles |
| Open Access |
| Special Issue Proposals |
| Guidelines for Authors |
| Guidelines for Editors |
| Guidelines for Reviewers |
| Membership |
| Fee and Guidelines |
 |
Promoting Regular Exercise as a Path to Obesity Treatment
Adeniji PO*
Department of Tourism Studies, Redeemer’s University, Ede, Osun State, Nigeria
Received Date: October 20, 2020; Accepted Date: November 07, 2020; Published Date: November 17, 2020;
*Corresponding Author: Adeniji PO, Department of Tourism Studies, Redeemer’s University, Ede, Osun State, Nigeria. Email: adenijio@run.edu.ng, aduk1012@yahoo.com
Citation: Adeniji PO (2020) Promoting Regular Exercise as a Path to Obesity Treatment. Adv in Nutri and Food Sci; ANAFS-201.
Abstract
Obesity, the condition of weighing 20 per cent or more above desirable body weight has been called one of the most serious nutritional problems globally. Despite the seemingly ubiquitous reports about benefits associated with regular exercise, there is evidence of non–responders to exercise due to genetic influence, food habits, overeating, unhealthy diets, wrong food choices, laziness, sedentary life, and other illnesses. Obesity is one of the preventable causes of death worldwide (mortality). Obesity increases the risk of many physical and mental conditions e.g. diabetes mellitus type 2, high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels (morbidity). Managing your weight is a big part of your health. Weight loss can be often being achieved through a healthy diet and exercise. Nutrition and Health Education is a problem of individuals in the developing world. This individual should examine and assessed their body mass Index (BMI) to identify their health problems. Health threats such as infectious diseases, malnutrition, cancer, diabetes, COVID-19, high blood pressure among others affect all of us naturally throughout the world resulting in morbidity and mortality. It is recommended that individuals’ general knowledge of nutritional information and physical education information should be increased through health programmes like physical exercise, sports and fitness, nutrition education, health and safety, healthy lifestyle and should be trained on how to calculate the body mass index (BMI) for weight control. Fruits and vegetables should be included in the daily diet of an individual e.g. oranges, pineapple, pawpaw, mango, water melon, cucumber, lettuce, cabbage, carrot to boost the immune system of individuals against diseases.
Keywords: Body Mass Index; Exercise; Nutritional problems; Obesity; Unhealthy diets
Introduction
Exercise is an activity intended to improve physical, or sometimes mental, strength and fitness (Oxford Dictionary, 2005). The health benefits of regular exercise and physical activity are hard to ignore regardless of age, sex or physical ability. When you engage in physical activity, you burn calories. The more intense the activity, the more calories you burn. Exercise can prevent excess weight gain or help maintain weight loss.
Engaging In Regular Exercise Would Grant People Various Health Benefits Such As:
Promoting better sleep: Regular physical activities will not make you struggle to fall asleep, but can help you fall asleep faster and deepen your sleep. Just don’t exercise too close to bedtime, or you may be too energized to fall asleep. Boosting energy: Regular physical activity can improve your muscle strength and boost your endurance. Exercise and physical activity deliver oxygen and nutrients to your tissues and help your cardiovascular system work more efficiently. And when your heart and lungs work more efficiently, you have more energy to go about your daily chores. Improving mood: There is the need to blow off some steam after a stressful day. A work out at the gym or a brisk 30 minutes’ walk can help. Physical activity stimulates various brain chemicals that may leave you feeling happier and more relaxed (See Figure 2). You may also feel better about your appearance and yourself when you exercise regularly which can boost your confidence and improve your self-esteem. It combats health conditions and diseases: Regular physical activity can help you prevent or manage a wide range of health problems and concerns, including stroke, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, depression, . And certain types of cancer, arthritis and falls. No matter what your current weight, being active boosts high – density lipoprotein (HDL), cholesterol and decreases unhealthy triglycerides and keeps your blood flowing smoothly, which decreases your risk of cardiovascular diseases. Exercise put the spark back into your sex life: Regular physical activity can leave you feeling energized and looking better, which may have a positive effect on your sex life. It can also lead to enhanced arousal for women and men who exercise regularly are less likely to have problems with erectile dysfunction than men who don’t exercise (WHO, 2009).

Figure 2: Fitness Exercise.
The bottom line of exercise and physical activity are a great way to feel better, gain health benefits and have fun. If you want to lose weight or meet specific fitness goals, you may need to exercise more. Remember to check with your doctor before starting a new exercise programme, especially if you have any health concerns. A sedentary lifestyle does the opposite, increasing the chances of becoming overweight and developing a number of chronic diseases (WHO, 2009).
Health according to World Health Organization (WHO, 2009) is a state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of disease of infirmity. At a minimum, health means freedom from physical, mental disturbances, emotional distress, spiritual discontent, social maladjustment and other negative states. At maximum, health means wellness (Aileen, 2005).
Obesity is abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that presents a risk to health (who.int./topics/obesity/en). The number one effect of eating unhealthy diet for many is weight gain which may lead to overweight and eventually obesity.
Structural Health refers to sound bones, muscles, organs etc. i.e. the structures in the body are properly performing the functions they were made for. Structural health is associated with a person’s height/weight ratio, the BMI (Body Mass Index), the resting pulse rate (heart rate), and the recovery time after doing exercise (Grossley, 2001). Body mass index (BMI) describes relative weight for height in people older than 20 years and correlates with degree of body fatness and disease risks. The margin provides the equation that is used to derive BMI values.
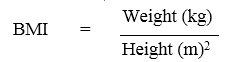
(Figure 1) shows the Body Mass Index (BMI) of healthy weight between BMI of 18.5 and 24.9. Most people within this range have few of the health risks typically associated with too-low or too-high body weight. Risks increase as BMI fall below 18.5 or rises above 24.9, reflecting the reality that both underweight and overweight impair health status. The BMI values also are most accurate in assessing degrees of obesity and are less useful for evaluating non-obese people’s body fatness (WHO, 2009).
Upper body fat is more common in men than in women and is closely associated with heart disease, stroke, diabetes, hypertension, and some types of cancer. In contrast, lower-body fat is more common in women than in men and is not usually associated with chronic diseases. Obesity is over-fatness with body mass index of 30 or higher with adverse health effects (Schattner and Shike, 2006).
Calculate your Body Mass Index (BMI)
Body Mass Index or BMI is the measurement for physicians and researchers studying obesity. A person’s weight in kilogram divided by height in meters squared is equal to BMI.
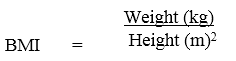
Excess weight could lead to development of serious health problems.
40 or greater = extremely obese
18.5-24.95kg/m2 = normal
25.0 – 29.9 kg/m2 = overweight
30.0 – 39.9 kg/m2 = obese
40 or greater = extremely obese
18.5kg/m2 or less = underweight
The Body Mass Index (BMI) describes relative weight for height in people and often correlates with degree of body fatness and disease risk. A person who takes measurement in kilograms and meters will calculate his/her BMI easily.
The BMI is therefore calculated as follows:

With this result, i.e. 19.35kg/m2, it can be concluded that the BMI of this individual is normal. If the BMI of an individual is greater than 30kg/m2, it means that an individual is obese and will need to lose weight (Figure 3).

 Figure 3: Obese Patient.
Figure 3: Obese Patient.
On the other hand, good chemical health means that the chemicals in the person’s body are correct, that tissues contain the right balance of nutrients and there are no toxic chemicals. This should be maintained by an individual who wants to live a healthy life.
Mental health refers to people’s cognitive and emotional well-being. According to WHO (2009), mental health is a state of well-being in which the individual realizes his or her own abilities, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and is able to make a contribution to his or her community.
Benefits of Fruits And Vegetables
Eating balanced diet (adequate proportion of each nutrient in daily diet) is important to good health. There are so many options available that we must continually decide which foods to select and how they are best prepared. The more complete the information we have concerning available foods, the easier it is to make the best choices for health (George and Pamploma, 2010). Food consumption should consist of fruits, vegetables, whole grains and fat-free or low-fat milk products. There have been a rapidly increasing number of scientific discoveries in recent years related to foods of vegetable origin. Fruit, grains, legumes and vegetables contain, in addition to nutrients found in all foods, two types of compounds that are found in foods of animal origin e.g. antioxidants (certain vitamins and minerals) and phytochemicals with curative properties. Type-2 diabetes, high cholesterol, high blood pressure and joint pains can be reduced by eating correct portions of balances meal coupled with physical activity. Promoting healthy eating through eating well will help people make healthy food choices to maintain healthy lifestyle (Burke et. al, 2009).
Some foods contain many of the same nutrients as others, and these foods are usually grouped together. For example, meat and fish, seeds and beans, nuts may be grouped together. All these foods are protein foods with the same nutrients. The nutritional value of foods in this food and food nutrients incorporated from each food group in your diet may help you remain in good health (MRJ, 2002).
There are five basic food groups that you can incorporate in your diet: (1) fruits (2) meat (3) vegetable (4) fish and beans and (5) milk including yoghurt and cheese. There are nutritional benefits from each group food consumed in a day. A healthy and balanced diet also contains a variety of foods from within each food group, since each food contains different macronutrients (the energy providing nutrients (carbohydrates, proteins and fats) and micro nutrients (vitamins and minerals). Eating a variety of foods also keeps our meals interesting and full of flavor. Grains contain carbohydrate, fibre and some vitamins and minerals. Whole grains are the healthiest choices. Examples of whole grain foods include whole wheat bread, oatmeal, whole grain crackes and breakfast cereals, whole wheat pasta, barley, brown rice and plain popcorn. Basic nutrients from the grains category are carbohydrates, fibre and some vitamins and minerals (Escott and Earl, 2008).
Sedentary lifestyle is associated with little or no physical activities in people. This can lead to overweight due to accumulation of fats. A healthy body weight is important for maintaining physical and emotional well-being and for preventing diseases.
Excess weight and obesity have been associated with the risk of numerous diseases like heart attack, high blood pressure, stroke, diabetes, osteoarthritis, some types of cancers, elevated blood cholesterol levels. Physical activity can provide health benefits that improve cardiovascular fitness, muscles, strength and body density (Bandura, 2005).
Discussion
This study assessed individuals on Body Mass Index (BMI). Nutrition, exercise and Health Education are an important aspect in the life of people to keep them fit. What people eat or drink, physical activity, and how they cope with stress plays an important role on our physical and mental well-being. People stay healthy or become ill often as a result of their own action or behavior on personal hygiene, balanced meal and other health related behaviours which make an individual keep fit and cope with stress (Galbally, 2004).
Individuals should be encouraged to avoid sedentary behaviour, plan their meals and eat adequately to maintain healthy lifestyle (Navarro, 2009). The number of worker who was overweight and obese is more than the workers who are normal. People should be discouraged eating junks during their break period. Some of the workers have nutritional diseases which can be cured by having correct information about planning, cooking and eating of meal.
It is interesting to note that adequate meal will work positively in the body; people should be encouraged to eat adequate meal with fruits and vegetables that can provide them with antioxidants to fight cancer. Broccoli contains indole-3-carbinol which can combat breast cancer by converting cancer-promoting estrogen into a more protecting type. Carrots can provide beta-carotene that help reduce lung, mouth, throat, stomach, prostate and breast cancer. Overweight and obesity can be reduced among workers if the intake of fruits and vegetables are higher. Mushrooms, avocados, grape fruits, papayas, tomatoes, apple can be of help to provide nutritional values that can fight different diseases.
Green tea and black tea are very good for fighting cancer. They contain antioxidants called polyphenol which can prevent cancer cells from dividing. Polyphenol are also found in the red wine and olives for protection against lung, colon, stomach, rectum, liver and pancreas. Physical activity is encouraged at least 30mins each day, about three days in a week. Nutrition education, health education, seminar on healthy lifestyle and counseling is encouraged to maintain healthy lifestyle. Regular physical activities according to WHO report (2009) make older adults who are active to have greater flexibility, weigh less, better balance, better health and live longer. Employees should be educated on the importance of good nutrition and physical activities to avoid risk of serious medical conditions which may cost the organization increasing amounts in medical costs, productivity, losses and absenteeism. Overweight and obesity are related health problems workers which are associated with Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) or heart failure. Access to healthy foods and regular exercises should be promoted among workers. Fruits and vegetables should be added to the diet on daily basis (Figure 4).


Figure 4: Fruits and Vegetables.
Conclusion
The paper highlighted the role of exercise in treating obesity. It shows from the discussion that this paper has increased the people’s knowledge on nutritional diseases, physical activity and how to calculate their Body Mass Index (BMI) to avoid overweight and obesity. It also led to change in their behaviour to make right choices of their food intake. In addition, it has changed the individuals’ behaviour on sedentary and unhealthy behaviour and lifestyle.
The paper increased the knowledge of individuals to include fruits and vegetables in their daily diet. The information gained during the course of the study by the people will help a lot to control their weight and engage themselves in one physical activity or the other to keep them fit.
Recommendations
- Workers should reduce inactivity for long periods, like watching television.
- Be physically active to maintain appropriate body weight.
- Continuous activities for your heart, lungs and circulatory system.
- Food is the best source of nutrients for everybody, supplements to foods, not substitutes for them; it is never too late to learn how to eat well.
- Avoid salty foods, sugary foods, fast foods and junks. Eat more fibres and less starchy foods.
- Sports and fitness, gymnastics sections should be put in place for workers in their places of work.
- Check your health status regularly.
- Choose activities you can enjoy can afford and can fit into your schedule.
- Consider bicycling, walking and gym.
- Watch video that shows exercise and practice.
- Build up slowly to a level of activity that makes you breath more heavily, increases your heart rate and makes you sweat.
- Build up exercises at least 30 minutes a day for a good cardiovascular health
- Drink extra water or sports drinks.
- Fruits and vegetables should be included in the daily diet of an individual.
References
- Aileen L (2005) Health Power (Health by choice) p. 117-110.
- Bandura A (2005) The Privacy of self-regulation in health promotion. Applied Psychology: An International Review, 54, No. 2: 245-254.
- Burke NJ, Joseph G, Pasick RJ, Barker JC (2009) Theorising social context: Rethinking behavioural theory. Healthy Education and behaviour, 36, suppl. 1:555-705.
- Crossley ML (2001) Rethinking psychological approaches towards health promotion. Psychology and Health, 16: 161-177.
- Escott Stump S, Earl R (2008) Guidelines for dietary planning. In LK Mahan, S. Escott-Stump, eds, Krause’s food, Nutrition and Diet Therapy, 12th Pp. 337-361. St. Louis Saundness Elsevier, 2008.
- Galbally RE (2004) Healthy minds, healthy bodies, and healthy nation: correcting education and health. Deakin West, ACT: Australian College of Education.
- Medical Research Journal (2002) Prevalence of overweight and Obesity among Urban Nigeria adults in Jos, Highland Medical Research Journal. 2002 1:1596-2407.
- Oxford Advanced Learners Dictionary (International Students’ Edition) 7th Pg 690. Oxford Press 2005.
- Navarro V (2009) What we mean by Social determinants of Health. Global health promotion, 16, No.1:5-16.
- World Health organizations, World Health Statistics Report 2009.
- int./topics/obesity/en/ Retrieved August, 2020.
- clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/11209-weight-cotrol-and-obesity/ Retrieved August, 2020.
- wikipedia.org/wiki/obesity. Retrieved August, 2020.
- Ranasinghe C, Gamage P, Katulanda P, Andraweera N, Thilakarathne S et al. (2013) Relationship between Body Mass Index (BMI) and body fat percentage, estimated by bio electrical impedance, in a group of Sni Lankan adults: a cross sectional study. BMC Public Health 13:1-8.