Publication Information
ISSN 2691-8803
Frequency: Continuous
Format: PDF and HTML
Versions: Online (Open Access)
Year first Published: 2019
Language: English
| Journal Menu |
| Editorial Board |
| Reviewer Board |
| Articles |
| Open Access |
| Special Issue Proposals |
| Guidelines for Authors |
| Guidelines for Editors |
| Guidelines for Reviewers |
| Membership |
| Fee and Guidelines |
 |
Apply Multiple Strategies to the Hand Hygiene Plan of Psychiatric Patients
Chin-Ling Chen1*, Yu-Chun Lin2, Ying-Chen Kao2
1Nursing head, Dept of Nursing, National Taiwan University Hospital Yunlin Branch
2Professional Nurse, Dept of Nursing, National Taiwan University Hospital Yunlin Branch
Received Date: November 07, 2021; Accepted Date: November 15, 2021; Published Date: November 22, 2021;
*Corresponding author: Chin-Ling Chen, Nursing head, Dept of Nursing, National Taiwan University Hospital Yunlin Branch. Email: chenchinlingy00560@gmail.com
Citation: Chen CL, Lin YC, Kao YC (2021) Apply Multiple Strategies to the Hand Hygiene Plan of Psychiatric Patients. Adv Pub Health Com Trop Med: APCTM-133.
DOI: 10.37722/APHCTM.2021401
Background
Chronic psychiatric patients live in groups, share facilities, have close contact with daily life, and have many opportunities to receive group treatments. Patients have dysfunction or deterioration due to disease factors, and their personal hygiene is often sloppy. They have differences in understanding and cognitive abilities, and are not in control of execution. The Ministry of Health is not sure and cannot actively express or request assistance. Infections in medical care will be caused by contaminated hands, the spread of infectious bacteria, cross-contamination of the environment and spread, which will lead to long hospital stays, high medical costs and high mortality. Studies have pointed out that the preventive medical care infection strategy is: wash your hands frequently and put them in the daily routine. It is the simplest, effective and most cost-effective measure to reduce the spread of pathogenic bacteria in medical institutions.
Methods
- Multi-game teaching strategy course-improve learning motivation and self-worth affirmation.
- Set the reminder voice to report the clock and draw the schedule of work and rest-concrete environmental treatment.
- Use singing faucets-cross-field cooperation, combine different professional fields, discuss issues together, and increase research and development efficiency.
- Establish a hand-guarded star officer-establish an audit system.
- Making teaching materials-multi-sensory learning with audio-visual animation.
Result
- Game learning brings life skills into the regularity of patients’ lives and improves the quality of self-care.
- Establish a lively and vivid learning environment centered on patients, and apply healthy behaviors in daily life.
- The family members affirmed the patient’s regular behavior and hand hygiene certification certificate after returning home.
- The incidence of infection density decreased and the effect was maintained.
- The completeness rate of inpatients performing hand hygiene increased from 79.9% to 92.2% and the accuracy rate of hand hygiene cognition increased from 80.2% to 100%.
Conclusions
Mental rehabilitation care uses group guidance and social skills training, through clear training goals, planned activity participation, repetitive practice, role playing, enhancement and modification of behavior. Using the concept of classroom game learning, the curriculum of multiple teaching strategies-professional knowledge is integrated into the game, and the flexible application of storytelling, competition and interactivity, etc., enhance motivation and correct cognitive feedback performance in the process, making it easier to achieve the goal.
Summary
Hands play an important role in the transmission of pathogenic bacteria. Hand washing is the simplest and most effective way to prevent nosocomial infections. Therefore, hand hygiene is the basic measure of infection control such as the health management of patients and staff and the prevention of infectious diseases. The purpose of the project is to improve the patient’s hand hygiene integrity rate. According to the analysis of the current situation, the reasons for the poor implementation of hand hygiene are low recognition accuracy of hand washing, low hand hygiene and cleanliness, no hand washing audit system and other factors. Formulate improvement countermeasures: 1. Multi-game teaching strategy course-improve learning motivation and self-worth affirmation. 2. Set reminder voice time, draw work schedule-specific environment processing. 3. Utilize singing faucet-cross-field cooperation, combine different professional fields, discuss issues together, and improve R&D efficiency. 4. Establish a full-time star official-establish an audit system. 5. Making teaching materials-multi-sensory learning audio-visual animation. After the implementation of the countermeasures, the patient’s hand hygiene integrity rate increased from 79.9% to 92.2%, and the accuracy rate of hand hygiene cognition increased from 80.2% to 100%.
Keywords: Game-Based Teaching; Hand Hygiene; Mental Health
Preface
Healthcare associated-infections, HAIs-related infections are the simplest, most effective and cost-effective method 1, 2, 3, 4. In 2020, the world will be raged by the COVID-19 epidemic and cause high mortality. To prevent the spread of the epidemic, all countries have called for People should pay attention to personal hygiene. In addition to wearing masks, frequent hand washing is also an important epidemic prevention measure. Chronic mental patients themselves have poorer personal hygiene and personal hygiene and self-care abilities, self-direction, language skills, and compliance with doctor’s orders than ordinary people. In addition, the space for public activities is limited. In the case of cluster infections, the difficulty of infection control and treatment will be higher than that of cluster infections in general wards.
Hands play an important medium in the transmission of pathogenic bacteria. Therefore, hand hygiene is a basic measure for the health management of patients and staff, and the monitoring and prevention of infectious diseases and other infection control measures; to implement the correctness and compliance of hand hygiene, Can reduce the chance of cross-infection of patients and staff3. The unit had two upper respiratory cluster incidents in the fourth quarter of 2019 and one upper respiratory tract cluster incident in May 2020. Although the three cluster incidents did not endanger the lives of patients, they did endanger the health and safety of patients. In addition, the current situation of new coronary pneumonia is severe, so the unit set up a task force to explore the reasons for clustering, implement the concept of infection control into daily work, and ensure the safety and health of patients and medical caregivers.
Current situation analysis
Brief introduction of the unit
This unit is a psychiatric chronic ward of a comprehensive teaching regional hospital with 54 beds, with an average bed rate of 89.6% and an average length of stay of 236 days. The majority of them are 32.8% with high school education, 75% are diagnosed as schizophrenia, and psychiatric symptoms are social Behavioral manifestations such as withdrawal and deterioration of self-care function. The staff are: 7 nursing staff including the chief nursing staff, and the manpower allocation of nursing staff: 2 nursing staff in normal day classes and 1 nursing staff in other periods; guardians are shared with the acute ward so there are 12 staff in total, and the unit has 3 manpower Configure 1 bit each. In addition to preventing patient interference, self-harm, and violent behavior, nurses also need to assist in daily life care, such as eating, toileting, bathing, changing clothes, and tidying up the environment. According to the particularity of the patient, conduct isolation, restraint and close inspection Room; guardian staff as assisting nursing staff, such as: maintaining the safety of the unit, supporting the safety of other psychiatric wards, counting the number of meals and issuing meals. This unit is a closed ward: a total of 18 wards with 3 people, and the remaining spaces: male hall, female hall, functional treatment room (also serving as a restaurant) and nursing station. Patients usually live in the limited space of the ward. The scope of the patient’s interpersonal interaction is mainly in the lobby in front of the nursing station, supplemented by the corridor outside the ward; during weekdays opening hours (10:00-11:30, 14:00-15:30) group activities are arranged by the functional teacher, and male and female patients will meet Gather in the functional treatment room to participate in functional activities; during meal times, patients will go to the restaurant to have a group meal to facilitate observation of the patient’s eating situation and prevent choking. Equipment: A total of 21 sets of wet hand-washing equipment are installed in the toilets and restaurants in each ward, and dry-cleaning hand soap is provided to the nurses in the nursing station and on the nursing work vehicle.
The status of hand hygiene in chronic psychiatric patients
The norms of the work manual of the unit pointed out: Nursing staff should perform broadcast operations before meals, before taking medicine, and before and after activities, and patients should go to the bathroom or dining room to perform wet hand washing by themselves. This unit formulates routine daily life group training health education every Tuesday, and fixes the topic of health education in the first week of each month: hand hygiene, to describe the teaching and health education leaflet, and teach patients how to perform hand washing timing and procedures.
Collecting and analyzing the patient’s hand hygiene data
- The patient’s hand hygiene integrity rate: 2020/8/1, the task force and sensory supervisors will discuss and summarize and define the time when psychiatric patients should wash their hands based on the clinical situation, and formulate the content of the “Hand Hygiene Checklist for Chronic Patients in Psychiatry” It is: the timing, steps and precautions for the patient to perform hand washing. 2020/8/10-12 The task force selected a fixed hand-washing time-before the patient had lunch, and randomly selected 44 patients for observation audit. The results showed that the patient’s hand-washing time was 56.8% (75 person-times of hand-washing hours/ 132 person-times should perform hand washing total number of times), the hand washing steps and precautions of patients who performed hand washing were audited, and the result showed that the completeness rate was 79.7% (calculation by formula: correct hand hygiene = number of times of correct hand hygiene/actual hand hygiene) Health times×100), Further interviews and analysis of the reasons: the content of the nurse’s lectures is 45.5% (20/44) if you don’t understand it, 22.7% (10/44) if you don’t know when to wash your hands, and it is 18.2 if you want to wash your hands casually. % (8/44), and I don’t know how long it takes to wash is 13.6% (6/44).
- Correct rate of patients’ hand hygiene awareness: 2020/8/1, the task force developed a “Psychiatric Patient Hand Washing Awareness Test Form” based on the Hand Hygiene Work Manual and literature of the Ministry of Health and Welfare. On 8/8/15, 2020, 44 patients will take a hand health care cognition test. The test will be presented with right and wrong questions, with a total of 10 questions. The results showed that the average correct rate was 80.2% (calculated by formula: cognitive correct rate of hand hygiene = cognitive correct items/total items × 100). Among them, the lowest three items are: the effect of hand-washing has nothing to do with the length of hand-washing time is 40.9% (18/44); when the hands are obviously dirty, you can use dry-cleaning hand soap to wash your hands is 61.4% (27/44); as long as soap Spread on your hands without rubbing it until foaming, and it can be 75% (33/44) after flushing.
- Nurses supervise the patient’s hand hygiene: 2020/8/16-25 actually observe 7 nurses supervising patients to perform hand hygiene, and found that: The timing and steps of the patient’s hand washing were not supervised 42.8% (3/7); The teaching method of group health education is only verbal teaching 28.6% (2/7). Furthermore, it was discovered that there is no audit system for nurses to supervise the patient’s hand hygiene, resulting in inaccurate supervision.
- Environmental equipment: On 2020/8/16 inspection of the wall of the washbasin in the restaurant, it was found that no hand-washing slogans were posted: while the hand-washing slogans in 18 wards were completely posted, 8 were damaged, and no hand-washing slogans were found in 2 rooms.
Problem and Cause establishment
Based on the above analysis and analysis results of the current situation, it is concluded that 79.7% of chronic patients in psychiatric department perform hand hygiene integrity rate. The main reasons are: (1) Nurses only use oral teaching to make patients unable to understand, and fail to urge patients to wash hands on time, resulting in hand washing. The cognitive accuracy rate is low; (2) Patients think that it is good to wash their hands if they are wet and do not know how long to wash them, and the imperfect hand-washing slogans post imperfect hand-washing steps; (3) There is no hand-washing audit system.
Project purpose
Because there is no relevant literature and research that can refer to the target value of hand hygiene integrity rate for chronic psychiatric patients, and there is no other information that can be used as the basis for benchmarking, after group discussion, the current situation of the unit and the patient’s disease factors are considered, and it is expected to follow The current level is increased by 50% as the target value, so the purpose of the project: the completeness of hand hygiene of chronic psychiatric patients has been increased from 79.9% to 89.9%. Goal setting value formula: goal value=improvement rate of complete hand hygiene of former psychiatric patients + (expected rate of complete hand hygiene of psychiatric patients x improvement ability), so 79.9 %+〔( 100%-79.9%) x0. 5〕=89.9%.
Literature verification
The importance of hand hygiene to psychiatric patients: In 2020, the Ministry of Health and Welfare pointed out in the guidelines on infection control measures for psychiatric institutions that frequent hand washing is the most basic anti-epidemic work, and the correct implementation of mechanical hand-washing actions and the timing of hand-washing , In order to minimize the number of dirty bacteria hidden between fingers, nails and fine lines. Psychiatric patients in the rehabilitation phase still have residual symptoms after treatment. Although the degree of interference is not as severe as the acute phase, the characteristics of the disease course affect the patient’s cognition and daily life management, and the ward environment is a closed, door-controlled, densely populated unit. Shared facilities, close and frequent daily contact, easy to be infected or cross-spread potentially deadly virus threats [3, 5]. The study points out that different strategies for improving hand hygiene habits can be combined through education to create a culture, reminder device, audit system, and incentive system, reducing barriers to hand hygiene, which is expected to increase compliance rates [5, 6, 7, 8].
Implement effective strategies for hand hygiene: Mental rehabilitation and nursing care should use group guidance and social skills training, through clear training goals, planned activity participation, repetitive exercises, role playing, enhancement and modification of behavior. Using the concept of classroom game learning, the curriculum of multiple teaching strategies-professional knowledge is integrated into the game, and the flexible application of storytelling, competition and interactivity, etc., enhance motivation and correct cognitive feedback performance in the process, and it is easier to achieve the teaching goals [9, 10, 11, 12]. Use situational simulation teaching, present in a realistic way through cases or situations, train learners to strengthen their impressions and modify behaviors, follow teamwork guidelines, and develop appropriate behaviors and attitudes [13]. The professional nursing characteristics of psychiatric nurses who have 24-hour contact with patients. If interactive learning can be used to clearly communicate health information and trigger behavior changes, it can improve patients’ deficiencies, apply healthy behaviors in daily life, and increase patient independence Sex and self-efficacy [3, 14, 15, 16]. Social skills training is a widely used nursing treatment in the clinical work of psychiatric departments to correct the behaviors of poor social interaction caused by withdrawal, shyness and psychological disorders [17]. Complete training can effectively improve the emotional expression, interpersonal interaction, social adaptation, quality of life and negative symptoms of mental patients, reduce social withdrawal, strengthen life adaptability, and build self-esteem, self-confidence and general coping skills [18]. Social skills training must first be approved by the patient, and after establishing feasible target behaviors for the case, reach a consensus with family members and cooperate with daily life exercises to encourage, support and affirm the progress of the disease. In addition, social skills training should be based on the principles of clear goals, simple to complex, and step-by-step. The five processes of explanation, demonstration, role-playing, feedback and positive enhancement and emphasizing repeated practice should be carried out in order, and the learning skills should be applied to daily life middle.
Solution and implementation process
- Solution: 4 members of the task force
Question establishment and discussion results, using the decision matrix diagram method, according to the feasibility, economy, efficiency of each countermeasure, etc., select the most suitable plan.
Planning period (2020/9/1-30)
- Construct a game-based learning curriculum-improve learning motivation and self-esteem: the project team invites staff to participate in game creation, and brainstorms the proposed learning curriculum from 1 to 2 pm every Tuesday from 9/1-30 (5 discussions in total)), design unplugged game methods: such as card games, board games and drawing, combined with accessories and rules such as boards, cards, chess pieces or small plates. After each game creation, all staff will hold a game test competition, use questionnaires as a tool to collect data, propose suggestions to modify the design, adjust the game mechanism, and formulate all game instructors, who need to be evaluated by the special team before they can be independent operate.
- Making an audio report clock and drawing a schedule of work and rest-specific environmental treatment: On September 1-30, the project team took into account the patient’s life and rest to present an autonomous law, produced an audio report clock after brainstorming, and designed a computer-voice software system combination The multi-function timer and alarm clock device uses an automatic control device to expect the patient to automatically run according to the predetermined rule according to the device process; draw a schedule for the patient to follow the daily routine and develop good living habits and self-care training. The 9/30 life seminar will be carried out after the publicity and the consensus start date.
- Making singing faucets-cross-field cooperation, combining different professional fields, discussing issues together, and increasing research and development efficiency: The 9/1-30 task force has no idea about the length of hand washing and rubbing time, in order to encourage extending the rubbing time , Wash hands thoroughly, cooperate with the work room in cross-fields, study the innovative nursing work of the National Federation of Nursing Professionals and Nurses Association of the Republic of China in 2007, and modify the tap switch module to calculate the time and guide the patient to perform the hand washing steps. The internal faucet controller IC panel, combined with music chip, infrared automatic sensor and automatic timer is modified.
- Planning and setting up a hand care value star officer-activity participation: The task force considers the patient’s ability and the consensus ability that the hand care value star officer should need, and plans to select the hand care value of this month during the life discussion on the first week of each month. Star officials conduct pre-employment training for situational simulation learning the next day, using role-playing, video teaching and discussion to guide thinking and correct behavior. In a situational simulation mode, arrange the hand care officer to audit the patient’s resistance situation and how to perform the hand hygiene audit in the process of the patient’s hand hygiene, so as to improve the hand care officer’s awareness of hand hygiene and the implementation of the skill score sex.
- Production of teaching materials-multi-sensory learning with audio-visual animation: 9/1-30 project team combined with sensory supervisors to review the timing and procedures of hand hygiene to make teaching materials. Taking into account factors such as the characteristics of the unit patient and age group, practice, experience, and reflect in the learning situation and imperceptibly. The patient-centered visual design perspective is produced. By listening and reading the graphic information, the patient’s vision, hearing and thinking are stimulated. Improve learning skills, make “Let’s Wash Hands” picture books, record hand hygiene DVDs and hand-washing 3D models.
Implementation period (2020/10/1-12/31)
- Implement game-based learning courses: group health education time, nurses will consider hand hygiene important Sex, timing and hand-washing steps are integrated into the game activities, such as: 10/6 “Hand-washing timing and fun”, 11/3 “Hand-washing puzzle matching card”, 12/1 “Hands clean-no residue”. Game methods, such as: “Clean hands-no residue” let everyone know the most neglected part of hand washing, and improve the effectiveness of hand washing. Game method: use group competition, first use fluorescent agent to smear your hands before the game, within one minute Wash your hands in the step of washing your hands. Finally, the group with the least amount of residual fluorescent agent will be the winner. The nurse will incorporate the game into the monthly group health education “Let’s wash hands together” course. The nurse will make a summary assessment after each patient’s participation in the group health education course, and use questioning strategies to guide the patient to say what’s wrong. Understand the points and clarify them in time to make relevant concepts more familiar, and the nurse will immediately issue rewards for encouragement on the same day.
- Use voice reporting clock and posting schedule: Since 10/3, nursing stations will place voice reporting clocks and use business jets to transmit automated program messages through Bluetooth. The content of the messages is based on the patient’s daily schedule. Reminders and implementation of functions such as broadcasting can share the work of nursing staff and save labor costs. When the system sounds: 8AM in the morning, 12 noon and 4:30 in the afternoon, remind patients that they need to wash their hands to prepare meals, and develop good habits; post the schedule in the announcement column-let the patient understand the fixed activity schedule, use the day clock-to The game method allows the case to point out the time to wash hands, use the concept of time and play to strengthen and supervise the meaning of the regularity of the life of the mental patient, maintain the ability of daily living, and strengthen the regularity of life.
- Use singing faucet: 11/15 install singing faucet in the restaurant faucet, the patient needs to touch the infrared detector with both hands, when the electronic infrared detection receives the signal, the hand washing procedure starts: the faucet will flow out water for 5 seconds to allow the patient to double When the hand is wet, when the music is played (set to YouTube “Hand Washing Song-Inner and Outer Clipping the Wrist” music), the tap will stop the water, and the patient will rub his hands according to the music lyrics until the music stops. After a total of 40 seconds, the faucet will bleed clean water again, and the patient will complete the hand-washing step after rinsing.
- Carrying out the hand care duty officer: 10/3 in the life discussion, the patient voted to serve as the one-month “hand care duty officer”. Job content: assisting in the distribution of hand washing milk, reminding the patient to complete hand washing and acting as a check on whether the patient is in Wash your hands properly when you wash your hands. A simple task is used to positively affirm the progressing patients, and the power of the hand-guarding star officer can arouse the attention and repercussions of other patients, which in turn promotes the ethos of hand-washing. On 10/5, a hand-care star officer simulation situation study will be held, so that the seed star officer can experience and imitate the learning behavior. After completing the checklist exam, the nurse will issue a hand hygiene master certification and a certificate of appreciation when he resigns next month. Set up a reward system for all patients, and design a hand-washing completion certificate: if the hand-washing inspection is performed at the end of each month, the number of points is more than 80, the head nurse will publicly praise and issue the hand at the first week of each month’s life seminar (11/3) Ministry of Health and Good Baby Commendation.
- Use teaching materials: From 11/1 onwards, the environment will be adjusted, using the activity flow chart as the conceptual model, and the three-dimensional map of the hand washing steps will be posted on the hand washing table as a visual reminder to teach the patient to complete the hand washing steps independently in order, and put the hand washing formula into Turned into a part of life; 11/5 “Let’s Wash Hands” picture book presents the frame of the story with patterns, mastering the situation and integrating effective and simple formulas and memories. It is successively produced and published in the way of daily life personal hygiene series, and is produced in a bimonthly way that is relevant to the patient’s daily life. Health education picture book, read by nursing staff; 11/15 3D model of hand hygiene steps is made and placed in the nursing station, so that patients can simulate the seven steps of hand washing, use visual art to penetrate into daily life and teach them hand washing skills; 11 /10 Before the morning exercises, the nurses’ self-made hand hygiene education video will be played, which is about the time to wash hands in daily life When & Why. In order to continue to implement the behavior, so that patients or family members can still watch and study online after returning home, the recorded video content is generated through the QR Code generator page to generate the QR Code of the video, placed on the unit health education poster board “Wash your hands and keep healthy”, and post it in the ward The bulletin board of the gate and the ward aisle is available for family members to download.
Evaluation period (2021/1/1-31)
- The recognition rate of hand hygiene of chronic patients in psychiatric department: According to the “Hand-washing Cognitive Test Form for Chronic Patients in Psychiatric Department”, the patients’ cognition level of hand washing after receiving game-based learning courses and using teaching materials is evaluated.
- Performing hand hygiene integrity rate check for chronic patients in psychiatric department: The task force evaluated the hand hygiene integrity rate of 44 patients in accordance with the “Psychiatric Chronic Patient Hand Hygiene Checklist” for 3 consecutive days to improve the project. Evaluate the implementation status of intervention measures.
Outcome evaluation
A project to improve the completeness of hand hygiene of chronic patients in psychiatry using game teaching and learning, environmental therapy, activity participation concepts and contextual teaching. After the countermeasures have been implemented, this project will be analyzed through the audit list and written test results, as shown in Figure 2.
- The recognition accuracy rate of hand hygiene of chronic patients in psychiatric department: 2021/1/1-31 task force evaluated 44 patients based on the “Psychiatric Patient Hand Washing Cognitive Test Form”, which increased the average recognition accuracy rate from 80.2% before improvement to 100%.

Figure 1: Awareness of hand washing in inpatients Straight line graph of comparison results before and after the test.
- Integrity rate of hand hygiene for chronic patients in the psychiatric department: January 1–31, 2021, according to the “Hand Hygiene Checklist for Chronic Patients in Psychiatry”. The timing of hand washing is 100%, and the hand washing steps and precautions of patients who have performed hand washing are audited. The results range from 79.9% before improvement to 92.2% after improvement, showing that the project goal has been achieved. The completeness rate of 2021/2/1-28 in the maintenance period was 90.1%. Reason analysis: The patient’s ability to take care of himself was reduced due to emotional interference. After a complete medical evaluation, the drug and dosage can be adjusted to maintain a stable state.
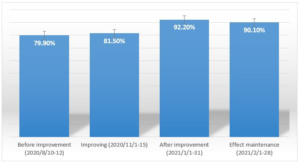
Figure 2: Histogram of comparison results of hand hygiene integrity rate of chronic patients in psychiatric department.
After the implementation of this project, the patient’s initiative in implementing hand hygiene has been significantly improved, and the steps can be correct. This shows that the use of game learning to bring life skills into the patient’s regularity of life can improve the quality of self-care. In February 2021, we will share the improvement results of this project at a meeting in the Department of Psychiatry, and will be launched in parallel in other chronic wards and day wards of psychiatric departments.
Discussion and Conclusion
From this project, it was found that the reasons for the poor implementation of hand hygiene by chronic patients in psychiatric department were the low recognition rate of hand washing and the lack of hand washing audit system. Although most patients have received hand hygiene-related courses, given that traditional teaching content cannot meet their needs, cross-team cooperation is used to improve teaching software and hardware equipment, and also promote the efficiency of teaching staff and the initiative of patients to learn Sex, enthusiasm, and accessibility of teaching materials. Establish a patient-centered lively and vivid learning environment and game-based learning, echoing the literature mentions that game-based learning has the effect of increasing memory and feedback. The completeness of hand hygiene in psychiatric chronic patients has increased from 79.9% to 92.2%. It can be seen that this project measure is suitable for hand hygiene programs and improving patients’ cognitive ability behaviors. During the project implementation period, the unit colleagues’ support and full participation, cross-departmental complementary skills, inspire and use creativity, patient-centered team form, work together for the patient’s treatment environment, which makes the clinical operation smooth and the project smoothly implemented as the project The biggest help: 2020/12/15 received a call from the health care nurse saying that when the home visit was conducted, the family members affirmed the patient’s regular behavior and the hand hygiene certification certificate issued by the hospital after returning home. This project is limited to the difficulty of obtaining the faucet switch module and the high cost (a set of faucets 5000 yuan and internal modification parts take time); when the patient line up for washing hands is too long and impatient, when there is a dispute, guard The staff need to support the guards across the floors, and the staff scheduling is the biggest resistance for this project.
Considering that digital learning is the trend of future education, it is recommended to train nurses to have a digital technology-based teaching model, receive information skills, digital teaching materials research and development and production training, so that teaching activities and the knowledge of diversified creative teaching materials can be internalized to obtain knowledge and then change behaviors. Arouse patient sympathy and obtain good learning results.
Reference
- Peng Mei-Tzi (2020) Nursing leads and speaks out: Guarding global health-From the viewpoint of Nightingale’s infection control, the prevention of new coronary pneumonia, Journal of Nursing, 67:103-110.
- Huang Wancui, Chen Yingying (2020) COVID-19 (Wuhan pneumonia) epidemic prevention war-the key to successfully defending Taiwan. Journal of Nursing, 15:75-83.
- Huang Xuanyi, Chen Ruilan, Hong Fenfang, Zhang Rongzhen, Li Chaoxiong et al. (2018) Most New Psychiatric Nursing (Ten Edition). Yongda.
- Stacy H, Cara G, Regi F, Shandra J, Rajkiran K et al. (2017) Patients’ Hand Washing and Reducing Hospital-Acquired Infection. Critical Care Nurse, 37:e1-e8.
- Ministry of Health and Welfare (2020, April 5). Guidelines for psychiatric institutions to respond to COVID-19 (wu pneumonia) infection control measures.
- Chen Yingchun, Shi Zhiyuan, Fu Renyunjie, Zhang Lvjuan, Wang Kaijun et al. (2014) Investigation on Hand Hygiene Knowledge, Attitudes and Behaviors of Medical Staff. Journal of Infection Control, 24:109-121.
- Lin YH, Liu CH, Chiu YH (2020) Google searches for the keywords of “wash hands” predict the speed of national spread of COVID-19 outbreak among 21 countries. Brain Behavior and Immunity. Advance online publication.
- Kathryn F (2018) Ten articles on hand hygiene innovation that have been reported in the Journal of Hospital Infection. Journal of Hospital Infection, 100:242-243.
- Lu Quefen, Wu Shumei, Xu Yingyu, Ye Meiyu (2018) Game-based learning in nursing education application-empathy board game teaching. Journal of Nursing, 65:96-103.
- Li Jiarong, Su Huiqi, Chen Baoru, Pan Wenling, Xiao Qilian et al. (2019) The effectiveness of game-based innovative teaching in high-alert drug training for new clinical nurses, New Taipei Journal of Nursing, 21:1-11.
- Xu Yuren, Yang Meijuan (2016) Using digital board games to explore the relationship between rational emotional beliefs, empathy and emotional decision-making styles. Educational Communication and Technology Research, 115:59-72.
- George A, Laura J, Joan M, Sheldon Benjamin, Jeffrey M et al. (2020) The American psychiatric association practice guideline for the treatment of patients with schizophrenia.177:868-872.
- Hong Shenghui, Wu Yonglong, Li Huizhen, Zhong Guobiao, Dong Yuqi et al. (2017) Discussion on the impact of high-realistic team simulation training on safety attitudes, behaviors and patient safety culture. Journal of Medical Management, 18:89-104.
- Keepers GA, Fochtmann LJ, Anzia JM, Benjamin S, Lyness JM (2020) The American Psychiatric Association Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry, 177:868-872.
- McDonald L (2018) Florence Nightingale, nursing, and healthcare today.New York, NY: Springer.
- Xiang YT, Zhao YJ, Liu ZH, Li XH, Zhao N et al. (2020) The COVID-19 outbreak and psychiatric hospitals in China: Managing challenges through mental health service reform. Int J Biol Sci, 16:1741-1744.
- Steven Wheeler, Amanda Acord-Vira, Diana Davis (2016) Effectiveness of Interventions to Improve Occupational Performance for People With Psychosocial, Behavioral, and Emotional Impairments After Brain Injury: A Systematic Review. American Journal of occupational therapy, 70:1-9.
- Anne Gordon, Penelope JD, Susan Patterson, Christopher AP, James GS et al. (2018) A randomized waitlist control community study of Social Cognition and Interaction Training for people with schizophrenia. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 57:116-130.